
Introduction to LEED Certification
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is an internationally recognized green building certification system developed by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC). LEED provides a comprehensive framework for designing, constructing, and operating environmentally responsible and energy-efficient buildings. Since its inception in 1998, LEED has become a global standard for sustainable construction, offering clear guidelines that help builders, designers, and property owners achieve sustainability goals while minimizing their environmental impact.
LEED is designed to address the environmental challenges posed by traditional construction practices. Buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption, carbon emissions, and waste production. LEED certification encourages the adoption of sustainable practices throughout the building’s lifecycle, from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
One of the core objectives of LEED is to create healthier indoor environments. By focusing on factors such as indoor air quality, natural lighting, and the use of non-toxic materials, LEED-certified buildings contribute to the well-being and comfort of occupants. Additionally, LEED fosters energy efficiency by encouraging the use of renewable energy sources, advanced HVAC systems, and intelligent energy management practices.
The certification process involves assessing a building’s performance across various categories, each of which reflects a critical aspect of sustainability. By achieving LEED certification, property owners demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship, operational efficiency, and occupant health.
Understanding the LEED Certification System
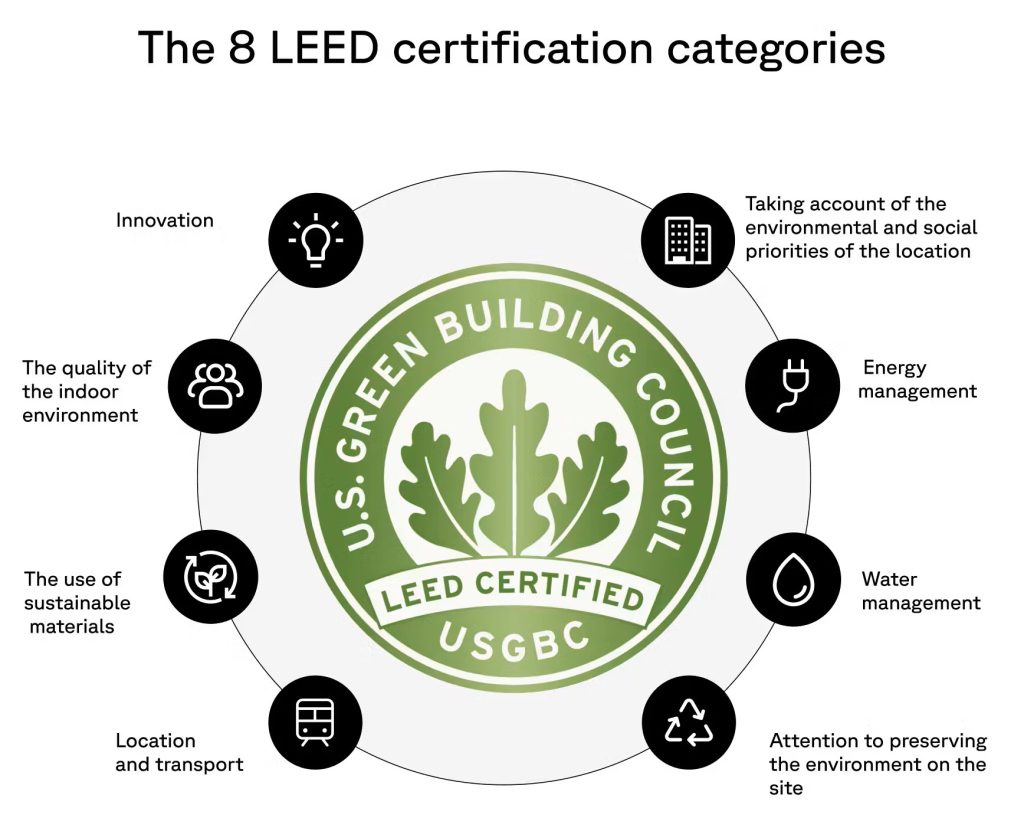
LEED certification is based on a point system that evaluates a building’s sustainability across multiple categories. Projects earn points by meeting specific criteria in these categories, which include:
- Sustainable Sites: Evaluates the impact of a building on the surrounding environment, promoting responsible land use, reduced site disturbance, green roofs, and access to public transportation.
- Water Efficiency: Focuses on reducing water consumption through efficient fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and sustainable landscaping techniques that minimize water usage.
- Energy and Atmosphere: Prioritizes energy efficiency through optimized energy performance, renewable energy sources, energy metering, and refrigerant management to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Materials and Resources: Encourages the use of sustainable materials, including recycled, locally sourced, and rapidly renewable materials. It also emphasizes waste reduction, material reuse, and responsible procurement.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensures a healthy indoor environment with high-quality air, natural lighting, low-emission materials, thermal comfort, and access to views. This category is critical as it directly impacts occupant well-being and productivity.
- Innovation: Awards points for innovative solutions and strategies that go beyond standard LEED criteria, encouraging creativity in sustainable design. These credits motivate project teams to think outside the box and develop pioneering practices.
- Regional Priority: Provides additional points for addressing environmental priorities specific to the project’s geographic location, ensuring locally significant issues are considered.
The purpose of C&D waste management is to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and promote sustainable practices. By recycling and reusing materials from demolished buildings, we can conserve natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and create new products. In Canada, C&D waste management is regulated by provincial and municipal governments. The regulations set guidelines for the handling, transportation, and disposal of construction and demolition waste. These guidelines are designed to ensure that the waste is managed safely and responsibly.
Projects that meet LEED criteria can achieve four levels of certification based on their total points:
- Certified (40–49 points)
- Silver (50–59 points)
- Gold (60–79 points)
- Platinum (80+ points)
Overall, C&D waste management plays an important role in promoting sustainability in the construction industry. By diverting waste from landfills and finding new uses for materials, we can reduce our impact on the environment and create a more circular economy. As consumers, we can also do our part by supporting companies that prioritize sustainability and recycling in their operations.

Comparing LEED Version 4.1 and Version 5
LEED Version 4.1 and Version 5 represent two major iterations of the certification system, each introducing updates aimed at improving sustainability in the built environment.
- LEED Version 4.1:
- Focuses on performance-based metrics rather than just design criteria.
- Enhanced energy efficiency requirements, including energy modeling and verification.
- Prioritizes indoor air quality, with updated standards for ventilation and low-emission materials.
- Expanded options for achieving points in various categories, providing flexibility.
- Transparency requirements for material ingredients through Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) and Health Product Declarations (HPDs).
- Updated strategies for water efficiency and building reuse, emphasizing lifecycle assessment.
- LEED Version 5:
- Expands its scope to address social equity, supply chain sustainability, and circular economy principles.
- Stricter requirements for energy efficiency, including a focus on net-zero energy and carbon reduction.
- Strengthens criteria for resource reuse, waste management, and material transparency.
- Introduces credits for social impact, biodiversity protection, and health and wellness.
- Enhanced digital tools for tracking sustainability metrics and certification processes.
- Incorporates advancements in building technology, including smart energy management and IoT integration for real-time performance tracking.
Loopico's Role in Achieving LEED Certification
Loopico, a platform dedicated to recycling construction waste, plays a vital role in helping construction projects achieve LEED certification. By providing a marketplace for buying and selling recycled construction materials, Loopico supports sustainable material management, which is a key aspect of LEED’s Materials and Resources category.
Key contributions of Loopico to LEED-certified projects include:
- Reducing Construction Waste: By diverting waste from landfills and promoting material reuse.
- Supporting Circular Economy: Facilitating the exchange of recycled materials, reducing the need for new raw materials.
- Enhancing Material Transparency: Ensuring that recycled materials meet LEED criteria for sustainability, safety, and traceability.
- Minimizing Carbon Footprint: By promoting the use of locally sourced recycled materials, Loopico helps projects reduce transportation emissions.
By leveraging Loopico’s services, construction projects can achieve higher LEED scores, particularly in categories related to waste management, material reuse, and sustainability.
-
loopicaco
- 3 Comments
3 Comments
Awesome
Cool partnership
Very good partnership